Подключение MCP3550 к arduino
- Войдите на сайт для отправки комментариев
Сб, 14/03/2020 - 20:22
Всем привет!
Мне нужно как можно точнее определить температуру. Поискав, нашел такую схему:
Собрал схему в proteus'е.

Нашел пример кода работы с этой микросхемой
// Arduino program to read Microchip MCP3550-60 using SPI bus // by John Beale www.bealecorner.com Feb. 9 2012 /* ======================================================= MCP3550 is a differential input 22-bit ADC (21 bits + sign) +Fullscale = (+Vref -1 LSB) = 0x1fffff -Fullscale = (-Vref) = 0x200000 1 LSB => Vref / 2^21 for Vref=2 V, 1 LSB = 0.95 uV Datasheet Spec: noise = 2.5 uV RMS with Vref = 2.5 V measured results: Noise Test setup: Vdd = 5V, +Vin = -Vin = Vref/2, Zin = 500 ohms (2x 1k divider) with Vref = 0.500 V, RMS noise = 8.60 LSB or 2.05 uV (1 LSB = 0.24 uV) with Vref = 1.000 V, RMS noise = 4.33 LSB or 2.06 uV (1 LSB = 0.48 uV) with Vref = 2.048 V, RMS noise = 2.16 LSB or 2.12 uV (1 LSB = 0.98 uV) with Vref = 4.00 V, RMS noise = 1.24 LSB or 2.37 uV (1 LSB = 1.91 uV) ========================================================== */ #include <SPI.h> // use Arduino SPI library #define CS 8 // bring CS high for ADC sleep mode, low to start new conversion #define MOSI 11 // MOSI is not used for this device #define MISO 12 // status and data bits from ADC #define SCK 13 // SPI clock from Arduino to ADC int samples = 100; // how many samples to group together for avg. and std.dev // MCP3550-60 does 15 samples per second (max) or 66.7 msec per sample void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); SPI.begin(); SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV32); // SPI clock rate < 5 MHz per MCP3550 spec SPI.setBitOrder(MSBFIRST); // MSB or LSB first SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE3); // rising/falling edge of clock digitalWrite(CS,HIGH); pinMode(CS, OUTPUT); // CS (out from Arduino) pinMode(MOSI, OUTPUT); //MOSI (data out from Arduino) pinMode(MISO, INPUT); // MISO (data in to Arduino) pinMode(SCK, OUTPUT); // SCK (serial clock) Serial.print("# MCP3550-60 ADC-Read v0.2 Feb.9 2012 sample size: "); Serial.println(samples); Serial.println("hours,value,stdev,min,max"); } // end setup() void loop() { byte r1, r2, r3, r4; byte OVL, OVH; // overload condition HIGH and LOW, respectively unsigned int i; // loop counter unsigned long w; long x; long minval, maxval; double sum, mean, m2, delta, sumsq, variance,stdev; double hours; sum = 0; sumsq = 0; m2 = 0; mean = 0; minval=1E9; maxval=-1E9; for (int n=0;n<samples;) { digitalWrite(CS,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(100); digitalWrite(CS,LOW); // start next conversion delay(50); // delay in milliseconds (nominal MCP3550-60 rate: 66.7 msec => 15 Hz) i=0; // use i as loop counter do { i++; delayMicroseconds(50); // loop keeps trying for up to 1 second } while ((digitalRead(MISO)==HIGH) && (i < 20000)); // wait for bit to drop low (ready) w = readword(); // data in: 32-bit word gets 24 bits via SPI port OVL = ((w & 0x80000000) != 0x00000000); // ADC negative overflow bit (input > +Vref) OVH = ((w & 0x40000000) != 0x00000000); // ADC positive overflow bit (input < -Vref) if ((i < 10000)) { n++; x = w <<2; // to use the sign bit x = x/1024; // to move the LSB to bit 0 position if (x>maxval) maxval = x; if (x<minval) minval = x; // Serial.println(x); delta = x - mean; mean += delta/n; if (n > 1) { // from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Algorithms_for_calculating_variance m2 += delta * (x - mean); } } } // end for i.. variance = m2/samples; stdev = sqrt(variance); hours = millis()/3600000.0; // convert milliseconds to hours Serial.print(hours,4); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(mean); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(stdev); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(minval); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(maxval); Serial.println(); } // end main loop() // =================================================== // read one word from 22-bit ADC device MCP3550 unsigned long readword() { union { unsigned long svar; byte c[4]; } w; // allow access to 4-byte word, or each byte separately w.c[3] = SPI.transfer(0x00); // fill 3 bytes with data: 22 bit signed int + 2 overflow bits w.c[2] = SPI.transfer(0x00); w.c[1] = SPI.transfer(0x00); w.c[0]=0x00; // low-order byte set to zero return(w.svar); // return unsigned long word } // end readword()
В итоге в симуляторе arduino подвисает на этой части кода
w.c[3] = SPI.transfer(0x00); // fill 3 bytes with data: 22 bit signed int + 2 overflow bits
Кто знает в чем может быть причина, может я какую ни будь тонкость пропустил?

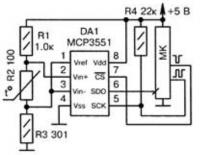
Тонкость - симулятор. В реале всё работает. По крайней мере вот этот кусок выдает код:
union{ int32_t myByteCode; uint8_t aByte[4]; }c ; digitalWrite(MCPPin,LOW); delay(76); SPI.begin(); SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV32); SPI.setBitOrder(MSBFIRST); SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE0); c.aByte[3] = 0x00; c.aByte[2] = SPI.transfer(0); c.aByte[1] = SPI.transfer(0); c.aByte[0] = SPI.transfer(0); SPI.end(); digitalWrite(MCPPin,HIGH); fl1=float(c.myByteCode);Задержку 76 мс подбирал специально для моего корпуса.
Благодарю за ответ.